
Internal Controls— A Strategic Asset for Financial Integrity
In today's age of digital banking, robust security measures are an absolute necessity for an organization to keep its data safe. Otherwise, internal data oversight, unauthorized transactions, financial misstatements, and cybercrime expose the business to huge financial losses and erode credibility.
This directs our attention to the topic of internal controls. Internal controls have a critical role to play in protecting an organization from financial and reputational loss. Organizations lacking proper internal controls experience rampant fraud, abuse, and waste.
However, there is a lot to cover about internal controls. Still, in this article, you will get a wholesome walkthrough on internal controls essentials that make an organization resilient to financial threats.
What are Internal Controls?
Internal controls across the organization form the backbone of the financial department. It serves as a fundamental component of the governance framework. These are the rules, procedures, and policies internal to the company.
Correspondingly, an internal financial control system encompasses the records and processes implemented by any firm to track capital, credit, and investment risks. Moreover, these are mandatory for a company to ensure accurate accounting management.
To further stress the importance of internal controls, many financial regulatory organizations consider internal controls indispensable. For instance, according to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) 2002, internal fraud deterrent systems are a must-have for publicly traded companies to protect investors from losing their money.
Effective internal controls ensure,
● Safeguard of assets
● Minimization of errors
● Either mitigation or nullification of risks
● Consistency across financial statements
All in all, beneficial operational and financial conduct to the company.
Preventive Vs. Detective Control
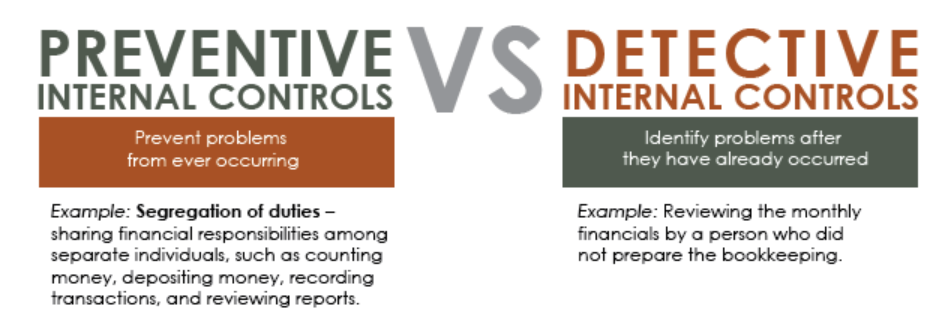
Preventive and detective internal controls are essential to an effective risk management strategy because they play complementary roles in safeguarding a company's assets and financial integrity.
As represented by the name, preventive control prevents fraud, errors, or misclassification, and detective control investigates and identifies them. Though preventive control is the primary thing to do to avoid irregularities before they occur, it needs to be followed up with proper measures of detective control to find those anomalies after their occurrence.
Preventive control is proactive in nature, while detective control is reactive. Another powerful way is to evaluate preventative control as an offensive plan or strategy against the opponent and detective internal control as a defensive strategy.
However, both act as monitoring systems to ensure a business's financial stability and operational efficiencies.
Weak Internal Controls and Financial Vulnerabilities
Organizations with weak internal controls leave the entire business vulnerable to financial risks. Due to this critical aspect, internal controls turn out to be a necessary discipline for any business. Therefore, establishing and promoting strong internal controls is a mission critical for long-term business success.
Within this frame of reference, it goes without saying that there exists a strong correlation between weak internal controls and financial risks of material errors, fraud, or misstatements. According to the report conducted by BDO, nearly 23% of all frauds came from accounting and sales departments. Lack of internal controls accounts for a total of 29% of frauds. Similarly, 20%of frauds occur because of overriding existing internal controls.
Development of an Effective Internal Control System
Effective internal control revolves around the interplay of risks and objectives. There exists an interchangeable relation between understanding the risk and setting the objectives. Below are some of the essential steps to follow to build an effective internal finance control system;
Risk Identification
Formulating effective internal control begins with understanding the risks the company is susceptible to. The appropriate understanding of risk lays the foundation for designing risk-mitigating internal control.
Control Environment Set-Up
Secondly, after assessing the risks there comes an appropriate setting of a strong control environment. Mostly, objectives are specific to the industry in which the business operates. Establishing clear procedures and policies is part of this step.
Segregation of Duties
The third fundamental to effective internal control is the segregation of duties. It involves separating financial function-specific responsibilities such as reconciling accounts and recording and authorizing transactions.
Controls Over Financial Reporting
The fourth step underlines the need to implement controls over financial reporting. This step is essential to ensure financial integrity via complete and accurate financial statements. Procedures for reconciling accounts, recording & processing transactions, and reviewing financial statements take effect at this stage.
Technology Deployment
At this point, technology is used as a potent tool for effectively implementing internal finance control. This can include automating financial processes through software, restricting access to financial information by establishing access control, and detecting potential frauds and anomalies by leveraging data analytics.
Review and Monitor
The final step integrates a system of checks and balances, maintaining oversight of areas of improvement and any required updates, thus ensuring the ultimate effectiveness of the internal control. This stage completes with the performance risk assessments, regular audits, and financial data analysis.
Internal Controls on Financial Risk Management
The internal control system is a versatile instrument pivotal to a company's long-term success. It is the foundation for an organization's financial stability, informed decision-making, and risk management. They ensure the company's security, reliability, and compliance with relevant regulations such as financial reporting standards.
Consequently, establishing a systematic approach and providing a framework for comprehensive control of the process landscape ensures regulatory compliance, helps mitigate risk, protects assets, and sustains resilience across the firm.
Moreover, internal controls play a vital role in;
Safeguard of Assets
Safeguarding a company's assets from theft, misuse, misappropriation, or unauthorized access. It happens with the segregation of duties, access control, and authorization.
Fraud Prevention
Supporting businesses in accounting, auditing, and reporting financial transactions in an accurate manner. This way, it prevents accidental financial errors and fraud.
Risk Assessment
Recording and evaluating potential financial risks. It helps develop proactive strategies to respond to the risks as they arise.
Effective Cash Flow Management
Identifying bottlenecks across business processes, ensuring efficient process flow for cash flow forecasting.
Conclusion
As business grows, the need for robust internal control grows alongside. The internal controls have a strategic advantage in enhancing financial reporting accuracy, regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, and proactive risk management.
Simply put, internal controls are all about taking measures that ultimately limit threats to the company's assets. It involves everything that takes over the risks to the company. The key takeaway is that the effective application of internal controls increases an organization's agility and efficiency towards its finances.




